What Is a Heat Sink? The Role It Plays in Cooling Your Devices
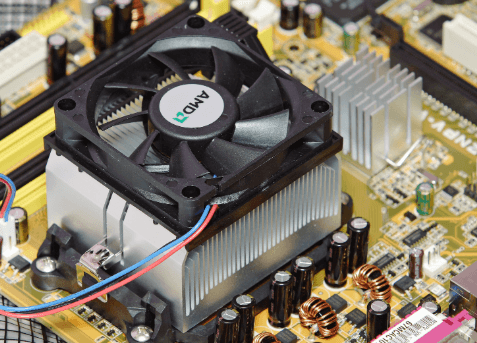
If you’ve ever asked what is a heat sink ,the answer lies in its vital role in keeping your devices cool and efficient. A heat sink is a component designed to absorb and dissipate heat from high-performance parts like CPUs, GPUs, and power transistors, preventing them from overheating. Without it, everyday devices such as computers, gaming consoles, and LED lights could lose performance, become unstable, or even suffer permanent damage. In this article, we’ll explain how heat sinks work, why they’re essential, and the impact they have on the technology you use daily.
What Is a Heat Sink?
A heat sink is a device that stops electronic parts, like CPUs, GPUs, or power transistors, from getting too hot. It absorbs extra heat and releases it into the air, keeping devices safe and working properly. Made from metals like aluminum or copper, which conduct heat well. They attach to parts that get hot and have fins or pins to spread out the heat, making it easier to cool the component.
Primary Function
The main job of a heat sink is to keep components at safe temperatures by:
- Pulling heat away from the component.
- Spreading heat across a larger area using fins or pins.
- Releasing heat into the air naturally or with the help of fans.
Heat sinks are essential for keeping electronic devices cool, reliable, and long-lasting.
How a Heat Sink Works
A heat sink prevents electronic parts from overheating by absorbing and releasing heat. Here’s how it works step by step:
Step 1: Heat is Generated
When components like CPUs or GPUs operate, they produce heat. Too much heat can damage them if it isn’t managed.
Step 2: Heat Moves to the Heat Sink
The heat travels from the component to the heat sink through conduction. A thin layer of thermal paste or adhesive often helps improve contact. Heat sinks are usually made of aluminum or copper because they conduct heat well.
Step 3: Heat Spreads Through the Fins
Heat travels from the heat sink’s base into its fins. The fins spread out the heat, letting it escape into the air. Their design determines how efficiently the heat sink cools.
Step 4: Heat Escapes into the Air
The heat moves from the fins into the surrounding air through convection. Warm air rises, and cooler air replaces it, carrying heat away from the heat sink.
Step 5: Airflow Boosts Cooling
- Natural airflow: Relies on air moving naturally due to temperature differences. Works well for low-heat devices.
- Fan-assisted airflow: A fan pushes air over the heat sink fins to remove heat more quickly. This is used in high-performance computers and electronic devices.
A heat sink transfers heat from a component and releases it into the air, with airflow enhancing its cooling efficiency.
Types of Heat Sinks
Heat sinks are essential for keeping electronic devices cool and can be grouped into three main types: active, passive, and hybrid.
- Active Heat Sinks
Active heat sinks use fans or pumps to quickly remove heat from electronic components. They are commonly used in devices that generate a lot of heat, such as gaming PCs, servers, and high-performance CPUs or GPUs.
Advantages
- Excellent cooling performance.
- Maintains stable temperatures even under heavy loads.
Disadvantages
- It can be noisy.
- Uses more power.
- Requires more maintenance due to moving parts.
- Passive Heat Sinks
Passive heat sinks don’t have any moving parts. They use natural airflow created by heat to release energy into the air. They are best for low-power devices like smartphones, IoT gadgets, and LED lights.
Advantages
- Silent operation.
- More reliable.
- Low maintenance.
Disadvantages
- Less effective for high-heat applications.
- May struggle in areas with poor airflow.
- Hybrid Heat Sinks
Hybrid heat sinks combine passive cooling with active cooling to remove heat more efficiently while staying quieter than fully active cooling systems.
Advantages
- Balanced performance and noise.
- Great for high-performance systems needing quiet cooling.
Disadvantages
- More complex and expensive.
- Active parts may fail over time.
Materials Used in Heat Sinks
Heat sinks are mainly made from aluminum and copper because both materials conduct heat well. The choice between them depends on the balance between performance, weight, and cost.
- Aluminum
Aluminum is the most commonly used material for heat sinks. It’s popular because it’s lightweight, affordable, and easy to shape, making it ideal for many electronic devices.
Advantages
- Lightweight and cost-effective.
- Good thermal conductivity.
- Easy to manufacture into complex shapes.
Disadvantages
- Lower thermal conductivity than copper.
- Not ideal for high-performance or high-heat systems.
Best for: Everyday electronics where keeping weight low and costs down is important.
- Copper
Copper transfers heat very well, making it great for high-performance cooling. However, it’s heavier, costlier, and harder to work with than aluminum.
Advantages
- Superior thermal conductivity.
- Excellent for demanding or high-temperature applications.
Disadvantages
- Heavier and costlier.
- Difficult to shape and manufacture.
Best for: Ideal for high-heat, high-performance devices.
Common Applications
Heat sinks remove excess heat, keeping electronic components safe and efficient across various industries.
- Computers and Laptops: Cooling CPUs, GPUs, and Chipsets
Heat sinks cool components by spreading heat and improving airflow. This prevents overheating and keeps the computer running reliably.
- Gaming Consoles: Stable Performance Under Heavy Load
Gaming consoles use heat sinks to control heat during intense gameplay. This prevents overheating, keeps performance steady, and protects the hardware.
- LED Lighting Systems: Longer Lifespan
LEDs are efficient and long-lasting, but still generate heat. Heat sinks absorb and release this heat to prevent overheating, maintain brightness, and extend the lifespan of lighting systems.
- Power Electronics and Automotive Systems: Handling High Heat
In cars, heat sinks cool components like inverters and engine control units. These components work in high-temperature environments, and effective cooling ensures the vehicle runs reliably and safely.
Heat sinks are essential for keeping electronic devices cool, reliable, and long-lasting. They prevent overheating and protect components, keeping electronic devices running reliably.
Why Heat Sinks Are Essential
Heat sinks are indispensable in modern electronics, ensuring devices operate efficiently and reliably. Here’s why they are essential:
- Prevent Overheating and Thermal Throttling
Electronic components generate heat during operation. Without effective heat dissipation, temperatures can rise to levels that cause components to throttle performance or even fail. Heat sinks absorb and dissipate this heat, maintaining optimal operating temperatures and preventing overheating.
- Ensure Consistent Performance and Reliability
Heat sinks stabilize temperatures, allowing electronic components to work efficiently without overheating. This reduces the risk of malfunctions or crashes, making devices more reliable.
- Extend the Lifespan of Electronic Devices
Excessive heat accelerates wear and tear on electronic components. By effectively managing heat, heat sinks reduce thermal stress, thereby extending the lifespan of devices and reducing the frequency of failures.
- Contribute to Quieter and More Efficient Cooling Systems
Heat sinks help cool devices without needing extra fans. This saves energy and keeps the system quieter.
Heat sinks are crucial for preventing overheating, ensuring consistent performance, extending device lifespan, and contributing to quieter and more efficient cooling systems.






